Sleeping Beauty (canoe) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
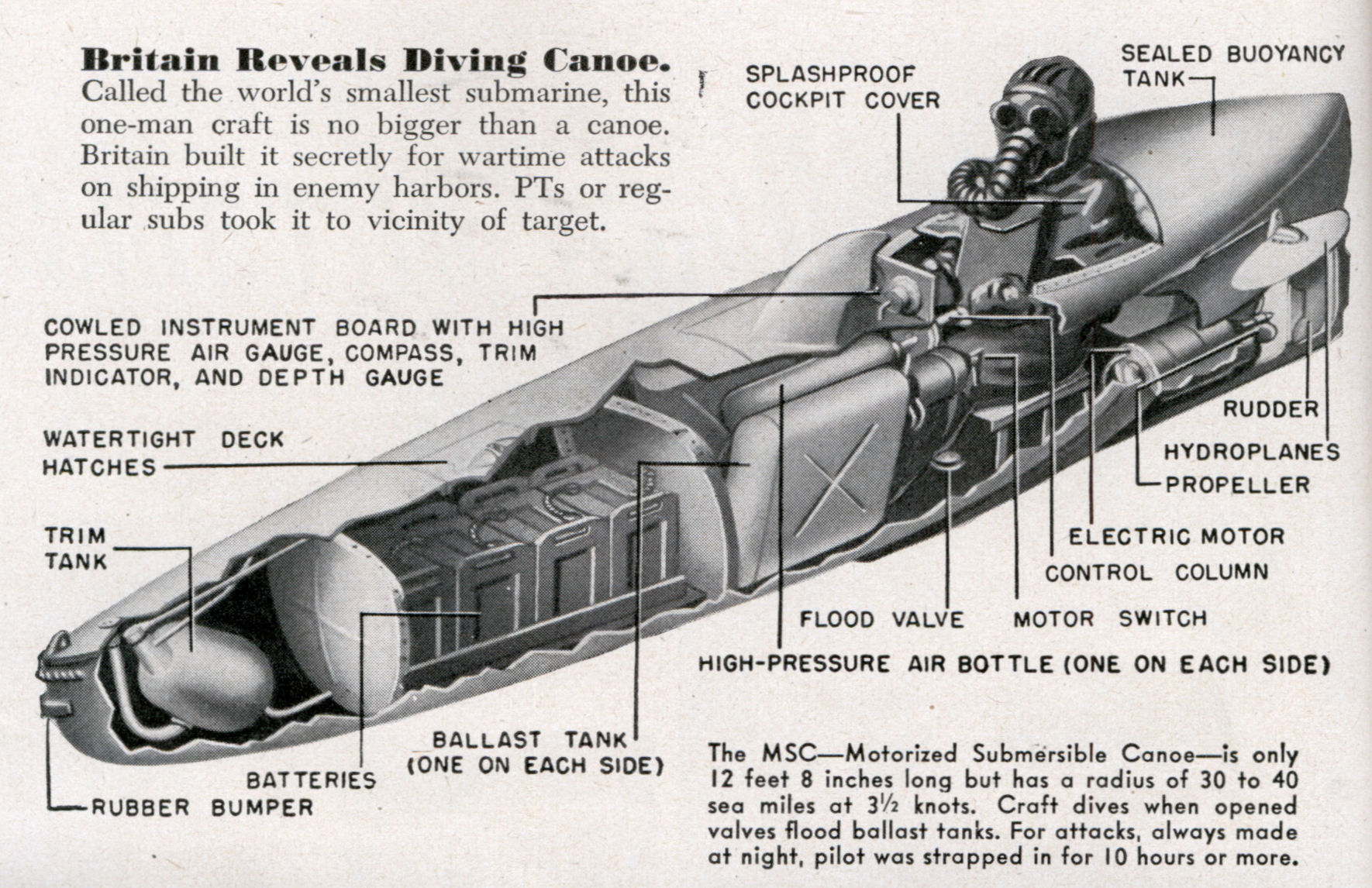
The Motorised Submersible Canoe (MSC), nicknamed Sleeping Beauty, was built by the British
 Constructed of
Constructed of
Image:Gal soe sleeping beauty.jpg
Image:Sleeping beauty underwater.jpg
Report on background and maritime archaeological survey for a Motorised Submersible Canoe (MSC) or ‘Sleeping Beauty’ lost 1945, HMAS Stirling, Careening Bay, Cockburn Sound
Maritime Archaeology Databases
mcdoa.org.uk
Sleeping Beauty – The Underwater Heritage Trust
British Special Operations Executive (SOE): Tools and Gadgets Gallery
BBC History World Wars: {{Underwater diving, divequ Midget submarines World War II submarines of the United Kingdom Wet subs British inventions
Special Operations Executive
The Special Operations Executive (SOE) was a secret British World War II organisation. It was officially formed on 22 July 1940 under Minister of Economic Warfare Hugh Dalton, from the amalgamation of three existing secret organisations. Its p ...
(SOE) during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
as an underwater vehicle
An underwater vehicle is any member of the class of vehicles (machines that transports people or cargo) that is intended to operate in the underwater environment. This article lists the types of underwater vehicle, with a brief description of eac ...
for a single frogman
A frogman is someone who is trained in scuba diving or swimming underwater in a tactical capacity that includes military, and in some European countries, police work. Such personnel are also known by the more formal names of combat diver, com ...
to perform clandestine reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops ( skirmishe ...
or attacks against enemy vessels.
Design
The MSC was designed by MajorHugh Reeves
Hugh Quentin Alleyne Reeves (1909-25 October 1955) was a British inventor and engineer. He was one of the most productive and creative engineers attached to Station IX the SOE research station during World War II.
Reeves was born at Seaford S ...
, R.E., who was also given the task of designing an 'unspecified device' for an underwater approach.Rees, 2008 based on an idea from Lt Col "Blondie" Hasler which he called the 'underwater glider' and developed at Aston House
Aston House was a prominent 17th century residence with large parkland situated opposite the parish church in Aston, Hertfordshire, UK.The house was demolished in 1961 by the Stevenage New Town Development Corporation after occupying it as its in ...
to Hasler's specifications. The craft got its nickname "Sleeping Beauty" when Reeves was found sleeping in it by a passing officer.
 Constructed of
Constructed of mild steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states:
* no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobal ...
, the canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the ter ...
is long with a beam of , used a 5 hp electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate f ...
powered by four 6-volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defin ...
batteries, had a top speed of , and could travel at a cruising speed of . Its maximum operating depth was .
The Sleeping Beauty was designed to carry up to of explosives
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
as well as being able to be dropped near its target by a heavy bomber
Heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of air-to-ground weaponry (usually bombs) and longest range ( takeoff to landing) of their era. Archetypal heavy bombers have therefore usually been among the larg ...
. Fore and central trimming tanks within the hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
can be flooded to sink the craft underwater or have compressed air blown in them to surface the craft. The pilot controlled the craft by a joystick that is connected to the rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally air or water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adve ...
and diving plane
Diving planes, also known as hydroplanes, are control surfaces found on a submarine which allow the vessel to pitch its bow and stern up or down to assist in the process of submerging or surfacing the boat, as well as controlling depth when subm ...
s, breathed through a Siebe Gorman Salvus
The Siebe Gorman Salvus is a light oxygen rebreather for industrial use (including by firemen and in coalmine rescue) or in shallow diving. Its duration on a filling is 30 to 40 minutes. It was very common in Britain during World War II and f ...
MkII Amphibian rebreather
A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen i ...
or Dunlop Underwater Swimming Breathing Apparatus (UWSBA), and would have to come close to the surface to establish his whereabouts. The canoe can also be paddled or moved by raising the mast
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio mas ...
and setting a sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails ma ...
. Although the Sleeping Beauty was designed to accommodate only one pilot, a later model did attempt to produce a two-man version post war. Different configurations were tried on the MSC such as the positioning of the hydroplanes; these were positioned aft, but sometimes moved forward during experimental work. The High Pressure air tanks (H.P.) could afford four blows to the surface from 40 ft and up to 20 blows to the surface from 15 ft.
During the end of 1943 the MSC was referred to the "Assault Warfare Sub Committee" (AWSC) and had trials conducted at Queen Mary Reservoir
The Queen Mary Reservoir is one of the largest of London's reservoirs supplying fresh water to London and parts of surrounding counties, and is located in the Borough of Spelthorne in Surrey. The reservoir covers and is above the surrounding are ...
. There the MSC was compared with the Chariot manned torpedo The Chariot was a British manned torpedo used in World War II. The Chariot was inspired by the operations of Italian naval commandos, in particular the raid on 19 December 1941 by members of the Decima Flottiglia MAS who rode "''Maiali"'' human t ...
and Welman submarine
The Welman submarine was a Second World War one-man British midget submarine developed by the Special Operations Executive. It only saw action once and was not particularly successful.
Design
Designed by the Commanding Officer of SOE's Inter S ...
. The MSC was found to be small (up to 15 canoes could be carried in a larger submarine's torpedo storage compartment), light, easier to navigate, simple to operate, and quick to build. However, the craft was very difficult to control.
Operation
The MSC's usual method of operations was "porpoising" in quick rises to the surface to check bearings, then shallow diving. This manoeuvre required the pilot to put the bow of the Sleeping Beauty to the water's surface and watch the reflection of it underneath the surface, and just when the bow was about to meet with its reflected image the Sleeping Beauty would be put into a dive so that the pilot's head would come out of the water and he was able to see his direction. The pilot could leave the Sleeping Beauty to swim and plantlimpet mines
A limpet mine is a type of naval mine attached to a target by magnets. It is so named because of its superficial similarity to the shape of the limpet, a type of sea snail that clings tightly to rocks or other hard surfaces.
A swimmer or dive ...
on enemy ships, rather than piloting the MSC to the target directly.
Operational service
MSCs were also used forOperation Rimau
Operation Rimau was an attack on Japanese shipping in Singapore Harbour, carried out by an Allied commando unit Z Special Unit, during World War II using Australian built Hoehn military MKIII folboats. It was a follow-up to the successful ''Ope ...
, a raid on Japanese shipping in Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
in September 1944 by commandos from the joint Australian, British and New Zealand Z Special Unit
Z Special Unit () was a joint Allied special forces unit formed during the Second World War to operate behind Japanese lines in South East Asia. Predominantly Australian, Z Special Unit was a specialist reconnaissance and sabotage unit that i ...
, sometimes known as "Z Force". After being found by a patrol boat, the canoes had to be scuttled along with the junk in which they were carried. Ten of the attacking force were taken prisoner by the Japanese and subsequently beheaded
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the au ...
.
A pair of MSCs are believed to have been captured by German forces after an unsuccessful attack on enemy shipping in Måløy
Måløy () is a town in the municipality of Kinn in Vestland county, Norway. Måløy is located on the southeastern side of the island of Vågsøy, about northeast of the village of Holvika and about south of the village of Raudeberg. The M ...
by members of the Norwegian Independent Company 1
Norwegian Independent Company 1 (NOR.I.C.1, pronounced ''Norisén'' (approx. "noor-ee-sehn") in Norwegian) was a British Special Operations Executive (SOE) group formed in March 1941 originally for the purpose of performing commando raids during ...
. The divers were landed with their canoes on the nearby island of Gangsøy. However, a local shepherd girl saw them and, thinking that they were thieving Germans, she reported them to the authorities. The divers were then chased across Norway by the Germans until they were picked up safely and taken back to their base in the Shetland Islands
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
.
In the summer of 1944, "Sleeping Beauty Number 72" was delivered to the United States Office of Strategic Services
The Office of Strategic Services (OSS) was the intelligence agency of the United States during World War II. The OSS was formed as an agency of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) to coordinate espionage activities behind enemy lines for all branc ...
(OSS), the forerunner of the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
, and became the early prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to ...
for today's Swimmer Delivery Vehicle
A diver propulsion vehicle (DPV), also known as an underwater propulsion vehicle, sea scooter, underwater scooter, or swimmer delivery vehicle (SDV) by armed forces, is an item of diving equipment used by scuba divers to increase range under ...
. It was used from December 1944 to August 1945 to evaluate United States harbour defences, stage mock attacks on capital ship
The capital ships of a navy are its most important warships; they are generally the larger ships when compared to other warships in their respective fleet. A capital ship is generally a leading or a primary ship in a naval fleet.
Strategic im ...
s and develop underwater communications equipment.
UCWE Trials Report on Sleeping Beauty
In November 1954, the Clearance Diving Trials Team attached to the Admiralty's Underwater Countermeasures and Weapons Establishment (UCWE) atLeigh Park
Leigh Park is a large suburb (population 27,500) of Havant, in Hampshire, England. It currently forms the bulk or whole of four electoral wards: Battins, Bondfields, Barncroft and Warren Park (generally referred to as 'The Warren').
Staunton C ...
House near Havant
Havant ( ) is a town in the south-east corner of Hampshire, England between Portsmouth and Chichester. Its borough (population: 125,000) comprises the town (45,826) and its suburbs including the resort of Hayling Island as well as Rowland's Cast ...
in Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
issued a report on the Sleeping Beauty, signed off by the Officer-in-Charge of the team, Lt Cdr Gordon Gutteridge RN:
Gallery
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * . *External links
Report on background and maritime archaeological survey for a Motorised Submersible Canoe (MSC) or ‘Sleeping Beauty’ lost 1945, HMAS Stirling, Careening Bay, Cockburn Sound
Maritime Archaeology Databases
mcdoa.org.uk
Sleeping Beauty – The Underwater Heritage Trust
British Special Operations Executive (SOE): Tools and Gadgets Gallery
BBC History World Wars: {{Underwater diving, divequ Midget submarines World War II submarines of the United Kingdom Wet subs British inventions